Science
Science at Langdon Park equips students with the tools needed to understand the world around them, explaining how things work and interact. Our curriculum empowers students with the knowledge of phenomena, enabling them to hypothesise and conduct experiments to prove scientific truths, predict outcomes and analyse causes.
Langdon Park’s KS3 curriculum secures a foundational knowledge base of fundamental concepts with concrete examples to make science real and relevant for our students. As our students progress to KS4 they revisit concepts and deepen their understanding of these concepts and appreciate the transferability of knowledge between the 3 disciplines as well as the importance of the scientific process in the progression of scientific thought.
Year 7 Science
Year 8 Science
Year 9 Science
Year 10 Science
Year 11 Science
T2-C7-Organic chemistry - What are the natural sources of raw material needed for our fuels?
T2-C8-Chemical Analysis -Can pure substances be detected using a flame test?
T3-C9-Chemistry of the atmosphere - Can we slow down global warming?
T4-P2-Why is electric charge a fundamental property of matter?
T4-P5- Forces-How do Forces Interact With Objects?
T4-P7- Magnetism and Electromagnets - Is the Earth’s magnetic field induced?
Year 12 Chemistry
T1 Amount of substance - How do chemists know how much ingredient to put in drugs?
T1 Atomic structure - What is inside the atom?
T2 Alcohols - What makes alcohols so reactive?
T2 Haloalkanes - How do halogens change the properties of carbonyl compounds?
T3 Alkenes - What makes alkenes different to alkanes?
T3 Grp 2 and 7 - How do the groups vary?
T4 Intro to aromatics- Why are organic compounds so important?
Year 13 Chemistry
Year 12 Physics
Unit 1: Particles - How has CERN helped to advance technology?
Unit 2: Quantum Phenomena -How has emission spectra improved our understanding?
Unit 3: Waves - What are the uses of EM waves in medicine and communication?
Unit 4: Mechanics -How has Newton’s laws of motion help us advance?
Unit 6: Electricity -Why are we moving over to Electric Cars?
Unit 7: Circular Motion - How does the ‘wall of death’ work?
Unit 8: Simple Harmonic Motion -How did engineers stop the Millennium Bridge wobbling?
Unit 10: Gravitational Fields - Why do satellites stay in orbit around the Earth?
Unit 11: Electric Fields -How does an ink-jet photocopier work?
Unit 12: Capacitors -How are capacitors used in electronic equipment?
Unit 13: Magnetic Fields and Electromagnetic Induction - How does a generator work?
Unit 15: Astrophysics (Physics) -How has Astrophysics increased our knowledge about Space?
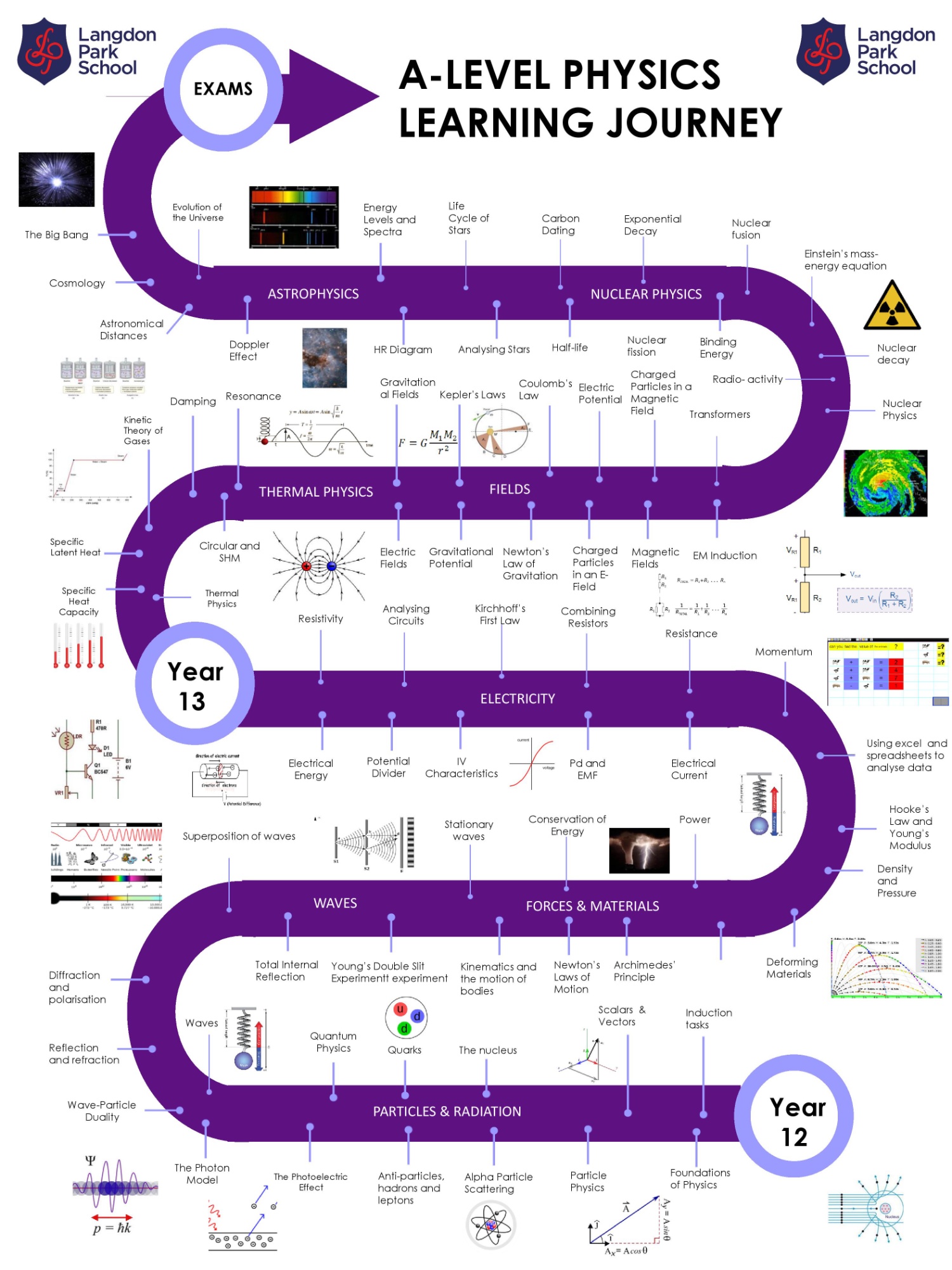
Year 13 Physics
T1.1 Why do gases behave like springs?
T 1.2 Gravitational Fields - why does the earth orbit the sun?
T1.3 Electric Fields How is a lightening bolt formed?
T1.4 Capacitors How is the energy stored in a camera flash?
T1.5 Magnetic Fields Why are charges deflected in a magnetic field?
T1.6 Electromagnetic Induction How is a phone charged wirelessly?
T2.1 Radioactivity What is nuclear medicine
T2.2 Nuclear Energy - Where is the nuclear energy in an atom
Year 12–13 Biology
